Read this blog if you want to know how to charge a Li-Ion battery using only a DC-DC converter.
Introduction
A Lithium-Ion battery is an indispensable power source for mobile applications. Li-Ions are lightweight, safe to use (with the necessary precautions), and are available in various capacities. They can also be connected in series to get your target voltage. With proper charge termination, you can charge Li-Ions safely over and over again.
Some CHARACTERISTICS of Li-Ion Batteries
Li-Ion’s typically have a nominal working voltage range of 3.6 – 4.2V. They come in different mAh capacities such as (2500, 5100 mAh, etc). A Li-Ion’s lower and higher-end voltages should be critically monitored for both extending the life of your batteries and safety. You should not go below 2.5V or you may risk shortening the life of your battery. If you go above 4.2V, your battery becomes a fire hazard.
There can be several types of Li-Ion batteries and they come in various forms. The example below discusses the 18650-battery type. The number relates to the dimensions of the battery which is close in form to a double (AA) battery, but bigger.

CHarging CHaracteristics of Li-Ion Batteries
Charging a Li-Ion battery normally requires 3 major stages. These stages are Constant current, Constant voltage, and Charge termination. Note that if your battery falls below 3V, you may need to initiate a “conditioning stage” (a constant current of about 0.1C) to ready your battery for the constant current stage.
Constant Current Stage
When you first charge a partially discharged battery (above 3V typical), you should go into constant current mode. You would typically need around 1C of your batteries’ capacity as charge current. This should go on until you reach the maximum potential of your battery which should be 4.2V
Constant Voltage Stage
After constant current, the next phase is constant voltage mode. At this stage, you should maintain the maximum potential of your battery at 4.2V. If you look at the charging current though, it should drop slowly. Let it drop until it reaches a certain threshold.
Charge Termination
The said current threshold determines the point of charge termination stage. This threshold should typically be small, about 1/10th of the charge capacity of your battery, or 0.1C. At this stage, you can terminate the charge cycle and declare your battery fully charged.
HOw to Charge a Single Cell Li-Ion using only a DC-DC Converter
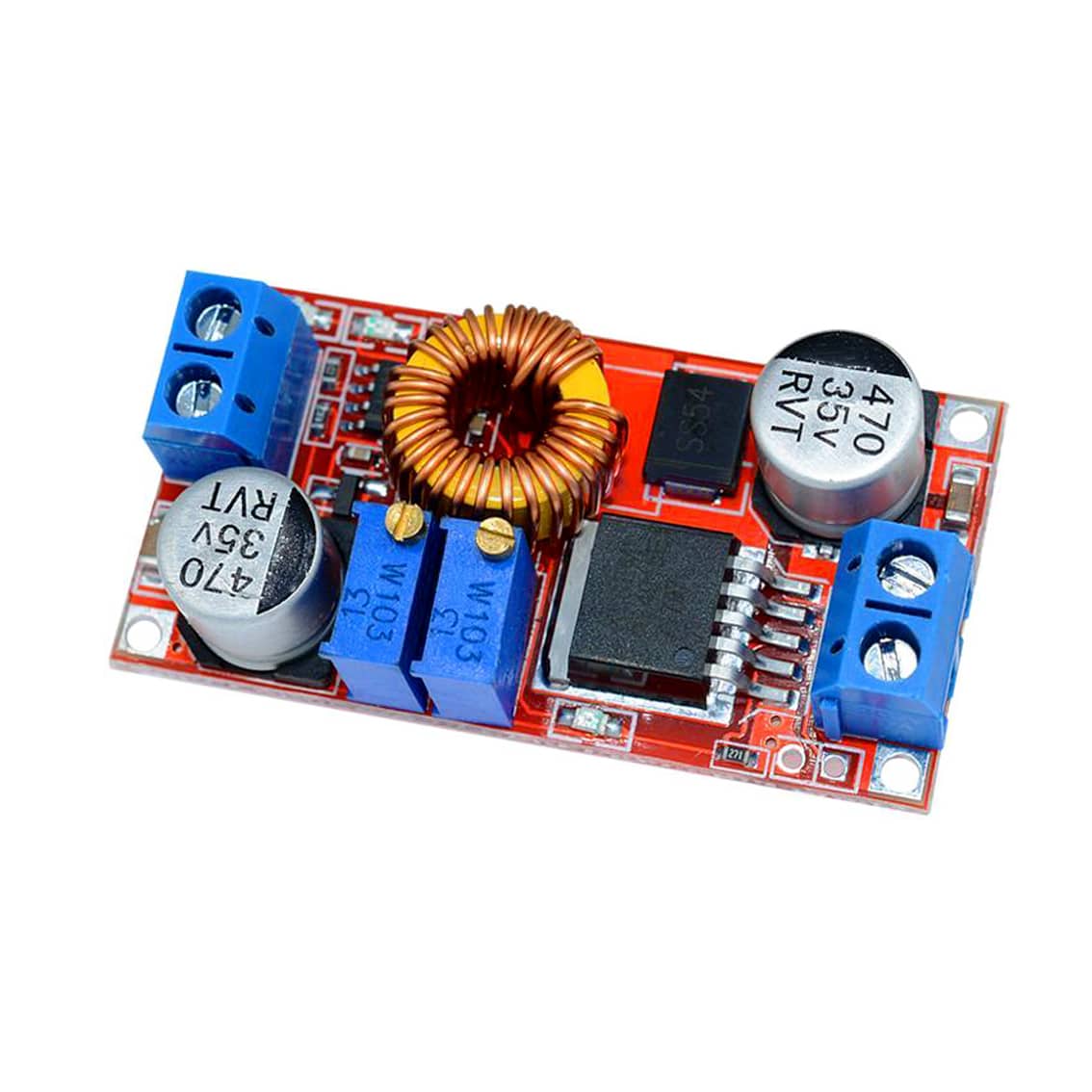
Several DC-DC Converter modules today are flexible in that they can be used in various configurations. These modules can act as constant voltage or current sources. With this, they come with a mode to become battery chargers too.
Below is a process from a popular DC-DC Buck Converter module to become a battery charger for both Li-Ion and 12V Lead Acid Batteries.
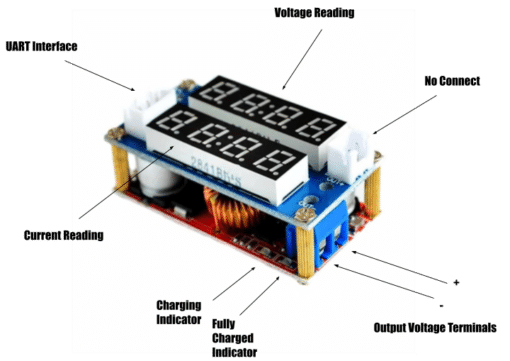
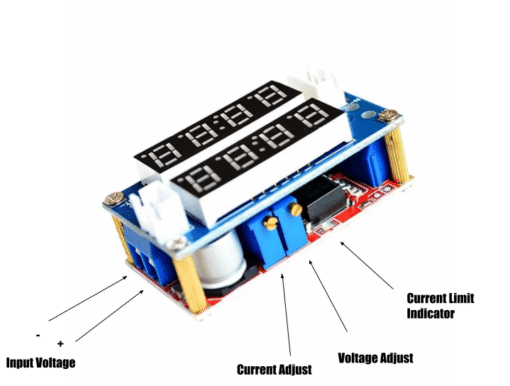
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
As a Battery Charger for Lead Acid or Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First, set the charging voltage by setting the Voltage Adjust Pot after applying power to the VInput Voltage terminals. The charging voltage is determined by your battery type. This can be 13.8V for lead-acid or 4.2V for Li-Ion.
- Next, short the output terminals and then adjust the Current Adjust Pot. You should see the Current Limit LED light up. Set the current as your constant current charge. This may typically be 25% of your rated rated capacity for lead acid or 1C for Li-Ion.
- Take off the short and hook up your battery. Your battery should start charging in constant current mode (indicated by the Charging and Current Limit Indicator).
- After that, you’ll end up in a constant voltage charge mode with the set voltage you set before (indicated when the Current Limit LED stops lighting).
- Finally, there will be so little current left (0.1C) in charging, indicating your battery is fully charged. The Fully Charged Indicator will light up to indicate this condition.
Note that the instructions above are for charging single-cell Li-Ion batteries. To charge several batteries, it’s recommended to add a BMS for safety concerns.
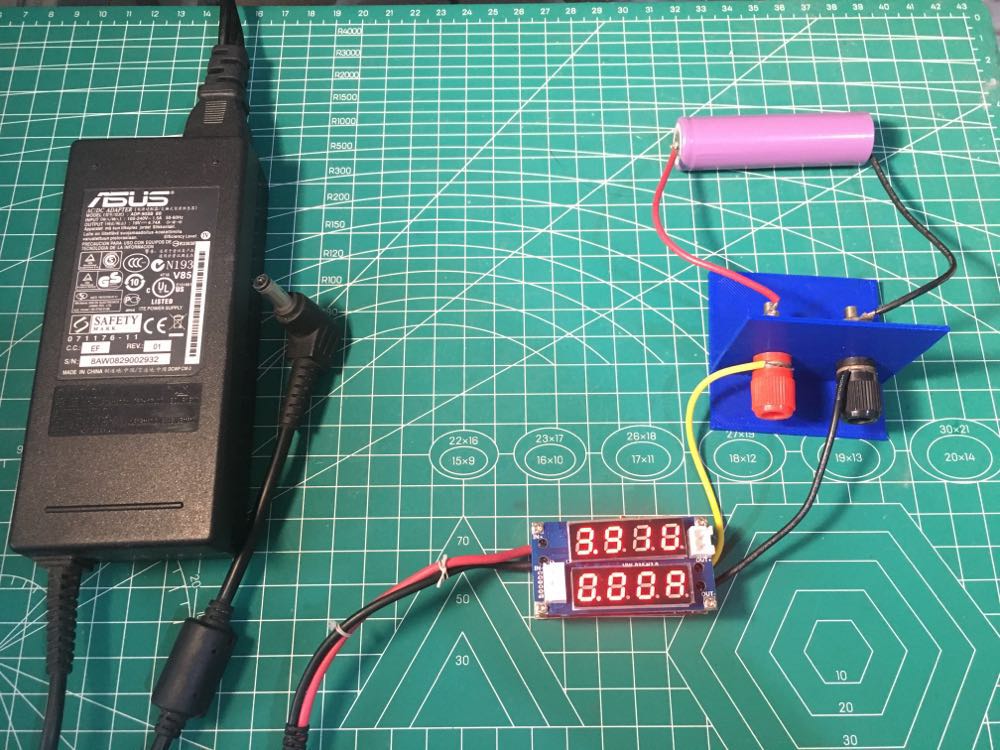
Charging Demo
Here, you can use a DC power source that is greater than the maximum charge voltage of 4.2V and the constant current value of 2.5A. Connect this power source o your DC-DC Buck converter input terminals.
Adjusting Max Charge Voltage
While not yet connecting the battery to the DC-DC, set the maximum charge voltage to 4.2V for a single cell Li-ion. Adjust it through the voltage adjust poentiometer.
ADJUSTING Constant Current Value
You can adjust the battery constant current value by shorting out the output of the DC-DC and then adjusting the constant current adjust potentiometer. Here, since we have a battery capacity value of 2500mAh, our constant current is 1C or 2.5A. Notice that the current limit indicator should light up.
constant Current Charge
When you connect a partially discharged Li-ion battery to the DC-DC, the charging process starts in constant current charge mode. Notice that the voltage display does not reach the maximum charge voltage yet. However, the current display is near the constant current value of 2.5A. At this stage, the current limit LED should be OFF while the while charging indicato should be ON.
Constant Voltage Charge
Here, you’ll notice that you are near constant voltage charge mode when the voltage display nears the maximum charge voltage (4.2V). Notice that the charging current continues to drop below the constant charge current at this stage.
Charge Termination
Charge termination happens when there is only a very small amount of current charging the battery (about 0.1C). Notice the fully-charged indicator lights up at this stage indicating that the charging process has finished. You may take out the battery during this time.
SHOP THIS PROJECT
-
DC-DC 20A 300W Adjustable Step Down Constant Current LED Driver Power Supply
$38.95Original price was: $38.95.$36.95Current price is: $36.95. Read more -
5A DC-DC Adjustable Step Down CC CV Power Supply Module with Voltmeter and Ammeter
$28.95Original price was: $28.95.$27.95Current price is: $27.95. Add to cart